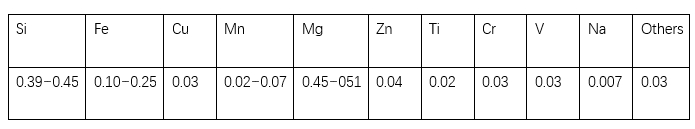
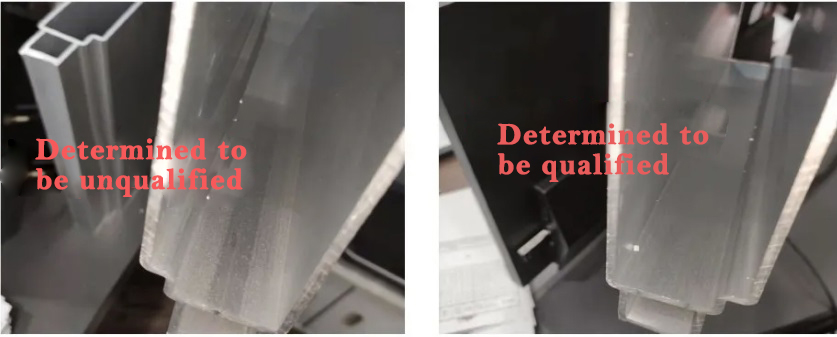
With the increasing awareness of environmental protection, the development and advocacy of new energy around the world has made the promotion and application of energy vehicles imminent. At the same time, the requirements for the lightweight development of automotive materials, the safe application of aluminum alloys, and their surface quality, size and mechanical properties are becoming higher and higher. Taking a EV with a vehicle weight of 1.6t as an example, the aluminum alloy material is about 450kg, accounting for about 30%. The surface defects that appear in the extrusion production process, especially the coarse grain problem on the internal and external surfaces , seriously affect the production progress of aluminum profiles and become the bottleneck of their application development.
For extruded profiles, the design and manufacture of extrusion dies are of utmost importance, so the research and development of dies for EV aluminum profiles is imperative. Proposing scientific and reasonable die solutions can further improve the qualified rate and extrusion productivity of EV aluminum profiles to meet market demand.
1 Product Standards
(1) The materials, surface treatment and anti-corrosion of parts and components shall comply with the relevant provisions of ETS-01-007 “Technical Requirements for Aluminum Alloy Profile Parts” and ETS-01-006 “Technical Requirements for Anodic Oxidation Surface Treatment”.
(2) Surface treatment: Anodic oxidation, the surface must not have coarse grains.
(3) The surface of the parts is not allowed to have defects such as cracks and wrinkles. The parts are not allowed to be contaminated after oxidation.
(4) The banned substances of the product meet the requirements of Q/JL J160001-2017 “Requirements for Banned and Restricted Substances in Automotive Parts and Materials”.
(5) Mechanical performance requirements: tensile strength ≥ 210 MPa, yield strength ≥ 180 MPa, elongation after fracture A50 ≥ 8%.
(6) The requirements for aluminum alloy composition for new energy vehicles are shown in Table 1.

2 Optimization and comparative analysis of extrusion die structure Large-scale power cuts occur
(1) Traditional solution 1: that is, to improve the front extrusion die design, as shown in Figure 2. According to the conventional design idea, as shown by the arrow in the figure, the middle rib position and the sublingual drainage position are processed, the upper and lower drainages are 20° on one side, and the drainage height H15 mm is used to supply molten aluminum to the rib part . The sublingual empty knife is transferred at a right angle, and the molten aluminum remains at the corner, which is easy to produce dead zones with aluminum slag. After production, it is verified by oxidation that the surface is extremely prone to coarse grain problems .

The following preliminary optimizations were made to the traditional mold manufacturing process:
a. Based on this mold, we tried to increase the aluminum supply to the ribs by feeding.
b. On the basis of the original depth, the sublingual empty knife depth is deepened , that is, 5mm is added to the original 15mm;
c. The width of the sublingual empty blade is widened by 2mm based on the original 14mm. The actual picture after optimization is shown in Figure 3.

The verification results show that after the above three preliminary improvements, coarse grain defects still exist in the profiles after oxidation treatment and have not been reasonably resolved. This shows that the preliminary improvement plan still cannot meet the production requirements of aluminum alloy materials for EVs.
(2) New Scheme 2 was proposed based on the preliminary optimization. The mold design of New Scheme 2 is shown in Figure 4. According to the “metal fluidity principle” and the “law of least resistance”, the improved automotive parts mold adopts the “open back hole” design scheme. The rib position plays a role in direct impact and reduces friction resistance; the feed surface is designed to be “pot cover-shaped” and the bridge position is processed into an amplitude type, the purpose is to reduce friction resistance, improve fusion, and reduce extrusion pressure; the bridge is sunken as much as possible to prevent the problem of coarse grains at the bottom of the bridge , and the width of the empty knife under the tongue of the bridge bottom is ≤3mm; the step difference between the working belt and the lower die working belt is ≤1.0mm; the empty knife under the upper die tongue is smooth and evenly transitioned, without leaving a flow barrier , and the forming hole is punched as directly as possible; the working belt between the two heads at the middle inner rib is as short as possible, generally taking a value of 1.5 to 2 times the wall thickness; the drainage groove has a smooth transition to meet the requirement of sufficient metal aluminum water flowing into the cavity, presenting a fully fused state, and leaving no dead zone at any place ( the empty knife behind the upper die does not exceed 2 to 2.5mm). The comparison of the extrusion die structure before and after the improvement is shown in Figure 5.


(3) Pay attention to the improvement of processing details. The bridge position is polished and connected smoothly, the upper and lower die working belts are flat, the deformation resistance is reduced, and the metal flow is improved to reduce the uneven deformation. It can effectively suppress problems such as coarse grains and welding, thereby ensuring that the rib discharge position and the speed of the bridge root are synchronized with other parts, and reasonably and scientifically suppressing surface problems such as coarse grain welding on the surface of the aluminum profile . The comparison before and after the mold drainage improvement is shown in Figure 6.

3 Extrusion process
For the 6063-T6 aluminum alloy for EVs, the extrusion ratio of the split die is calculated to be 20-80, and the extrusion ratio of this aluminum material in the 1800t machine is 23, which meets the production performance requirements of the machine. The extrusion process is shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Extrusion production process of aluminum profiles for mounting beams of new EV battery packs

Pay attention to the following points when extruding:
(1) It is forbidden to heat the molds in the same furnace, otherwise the mold temperature will be uneven and crystallization will occur easily.
(2) If an abnormal shutdown occurs during the extrusion process, the shutdown time must not exceed 3 minutes, otherwise the mold must be removed.
(3) It is prohibited to return to the furnace for heating and then extrude directly after demolding .
4. Mold repair measures and their effectiveness
After dozens of mold repairs and trial mold improvements, the following reasonable mold repair plan is proposed.
(1) Make the first correction and adjustment to the original mold:
① Try to sink the bridge as much as possible, and the width of the bridge bottom should be ≤3mm;
② The step difference between the working belt of the head and the working belt of the lower mold should be ≤1.0mm;
③ Do not leave a flow block ;
④ The working belt between the two male heads at the inner ribs should be as short as possible, and the transition of the drainage groove should be smooth, as large and smooth as possible;
⑤ The working belt of the lower mold should be as short as possible;
⑥ No dead zone should be left at any place ( the back empty knife should not exceed 2mm);
⑦ Repair the upper mold with coarse grains in the inner cavity, reduce the working belt of the lower mold and flatten the flow block , or do not have a flow block and shorten the working belt of the lower mold.
(2) Based on the further mold modification and improvement of the above mold, the following mold modifications are performed:
① Eliminate the dead zones of the two male heads;
② Scrape off the flow block;
③ Reduce the height difference between the head and the lower die working zone ;
④ Shorten the lower die working zone.
(3) After the mold is repaired and improved, the surface quality of the finished product reaches an ideal state, with a bright surface and no coarse grains, which effectively solves the problems of coarse grains, welding and other defects existing on the surface of aluminum profiles for EVs.
(4) The extrusion volume increased from the original 5 t/d to 15 t/d, greatly improving production efficiency.
5 Conclusion
By repeatedly optimizing and improving the original mold, a major problem related to the coarse grain on the surface and welding of aluminum profiles for EVs was completely solved.
(1) The weak link of the original mold, the middle rib position line, was rationally optimized. By eliminating the dead zones of the two heads, flattening the flow block , reducing the height difference between the head and the lower die working zone , and shortening the lower die working zone, the surface defects of the 6063 aluminum alloy used in this type of automobile, such as coarse grains and welding, were successfully overcome.
(2) The extrusion volume increased from 5 t/d to 15 t/d, greatly improving production efficiency.
(3) This successful case of extrusion die design and manufacturing is representative and referenceable in the production of similar profiles and is worthy of promotion.
Post time: Nov-16-2024